Search Result
Results for "
D-Glucose-<sup>13</sup>C,d-1
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
41
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B0389S10
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
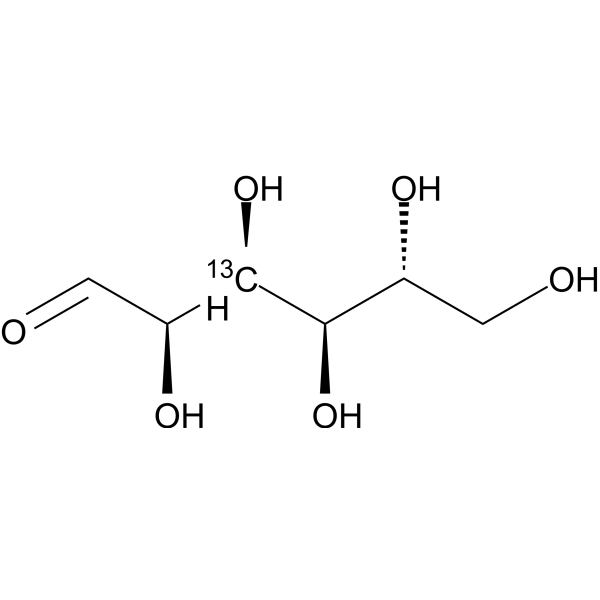
D-Glucose- 13C is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
-
- HY-W010042S
-
|
L-(-)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
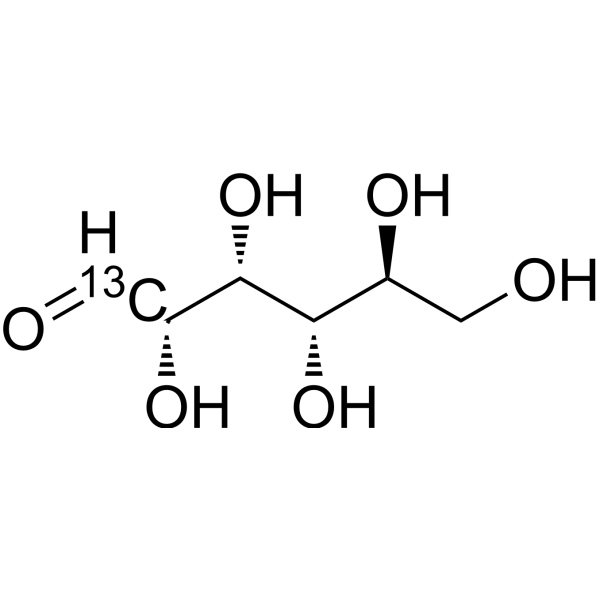
L-Glucose- 13C is the 13C labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose (L-(-)-Glucose) is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose can promote food intake[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-B0389S29
-
|
Glucose-<sup>18sup>O; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>18sup>O; Dextrose-<sup>18sup>O
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
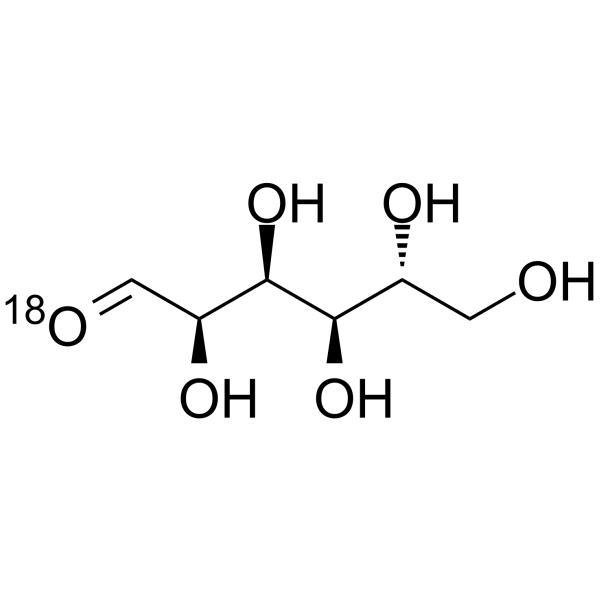
D-Glucose- 18O is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules
|
-
-
- HY-B0389S11
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-1; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-1; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C-1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
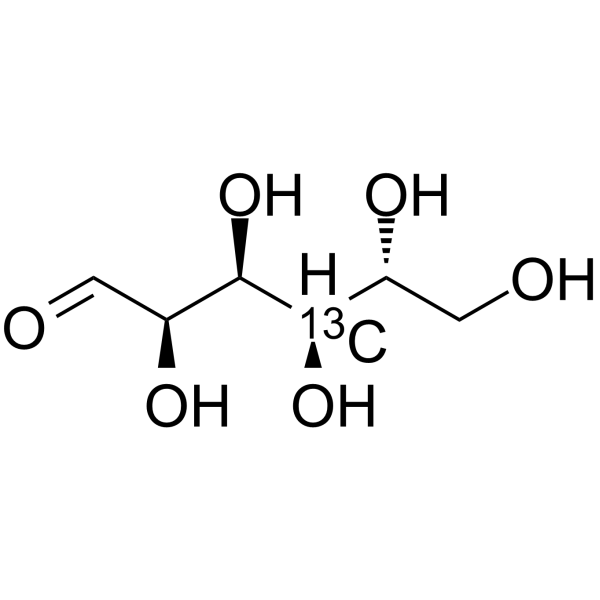
D-Glucose- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
-
- HY-B0389S12
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-2; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-2; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C-2
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-2 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
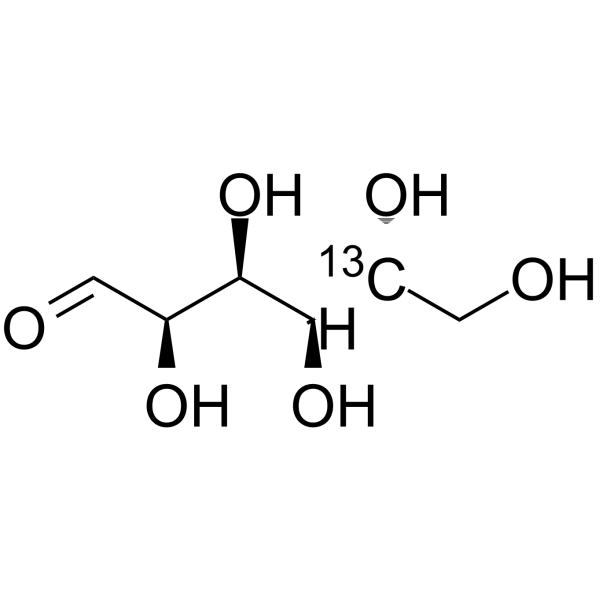
-
- HY-B0389S16
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-4; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-4; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C-4
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-4 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
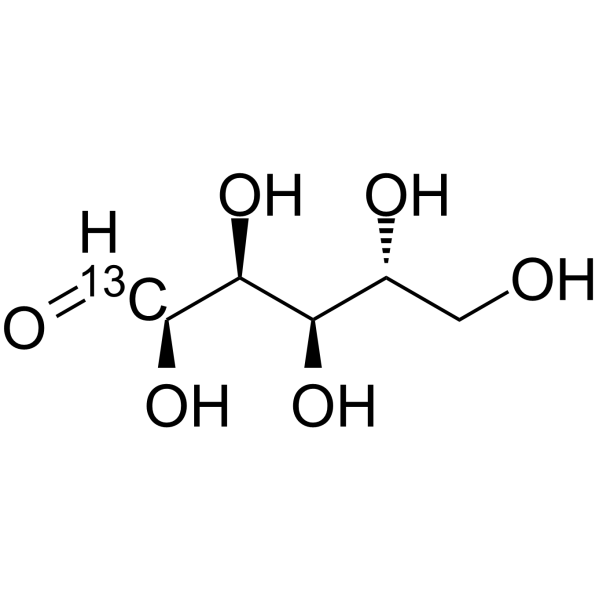
-
- HY-B0389S17
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-5; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-5; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C-5
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-5 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
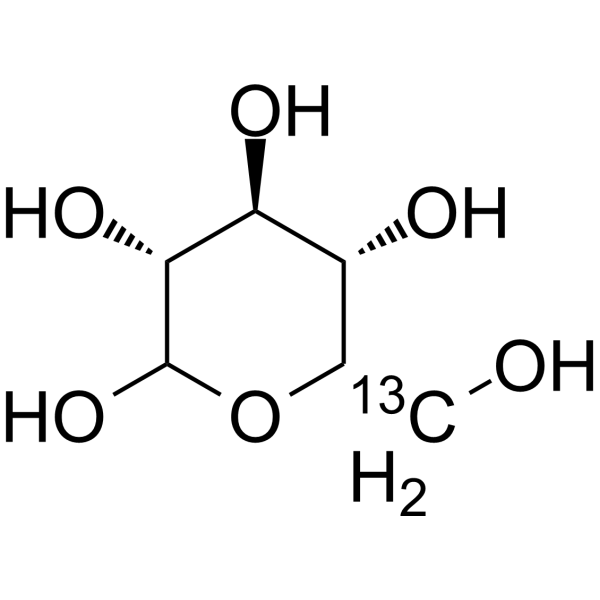
-
- HY-B0389S13
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-3; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-3; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C-3
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-3 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
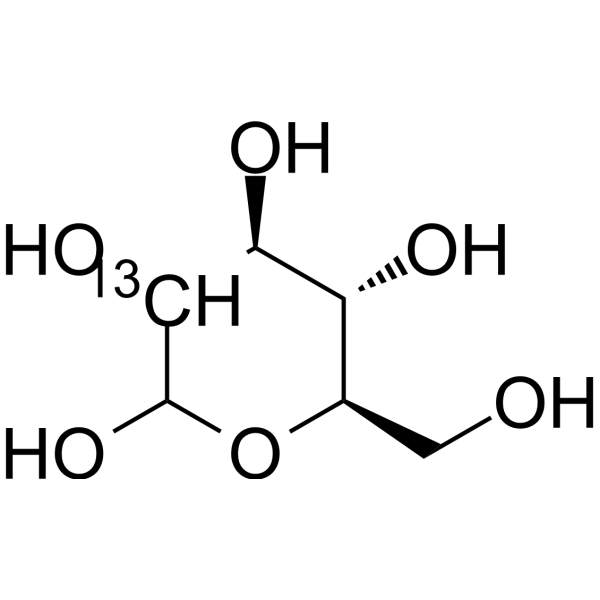
-
- HY-B0389S30
-
|
Glucose-<sup>18sup>O-1; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>18sup>O-1; Dextrose-<sup>18sup>O-1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O-1 is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecule
|
-
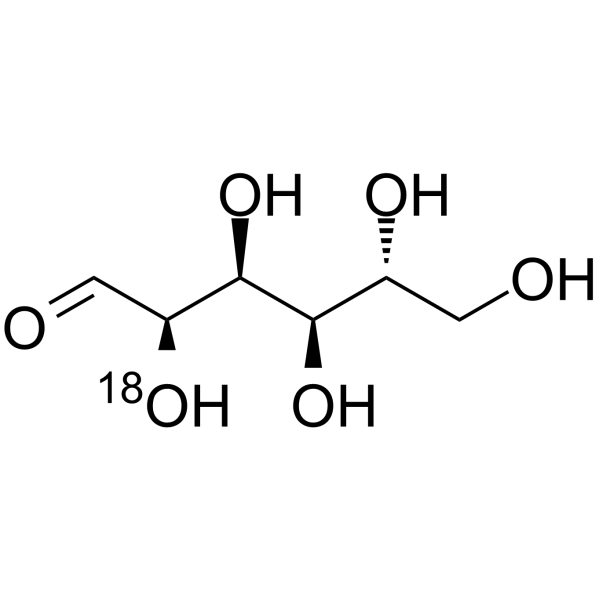
-
- HY-B0389S31
-
|
Glucose-<sup>18sup>O-2; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>18sup>O-2; Dextrose-<sup>18sup>O-2
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O-2 is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecule
|
-
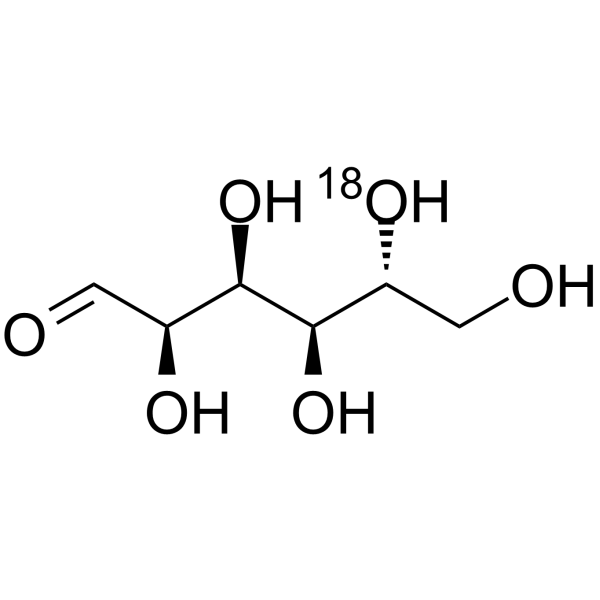
-
- HY-B0389S32
-
|
Glucose-<sup>18sup>O-3; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>18sup>O-3; Dextrose-<sup>18sup>O-3
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O-3 is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecule
|
-
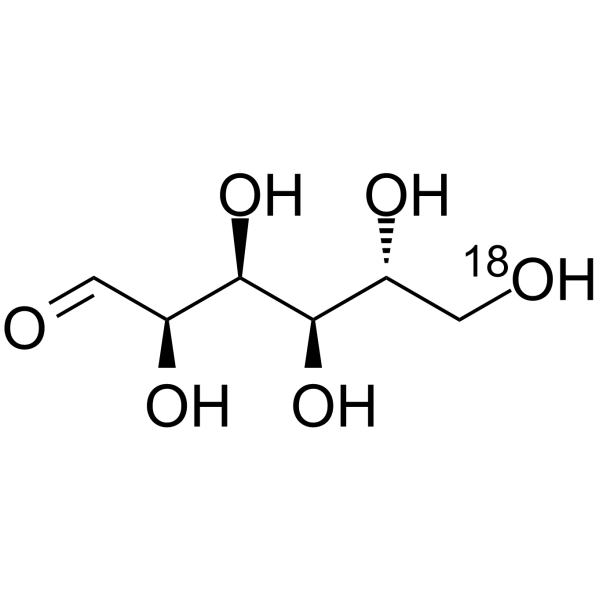
-
- HY-B0389S19
-
|
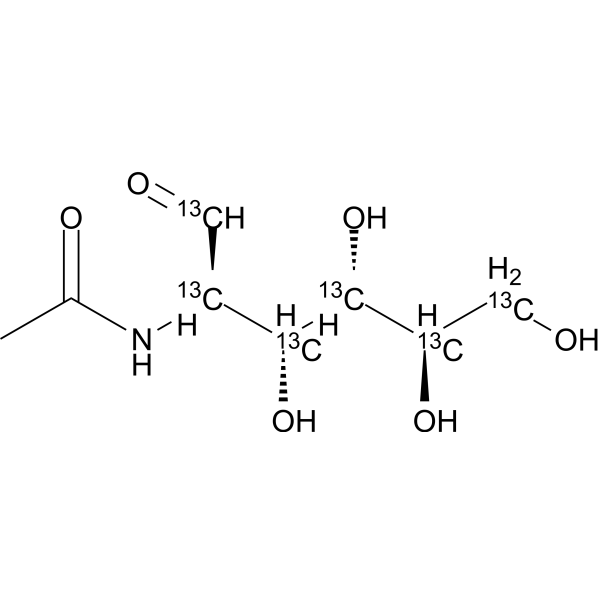
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,d; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,d; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C,d
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C,d is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical sign
|
-
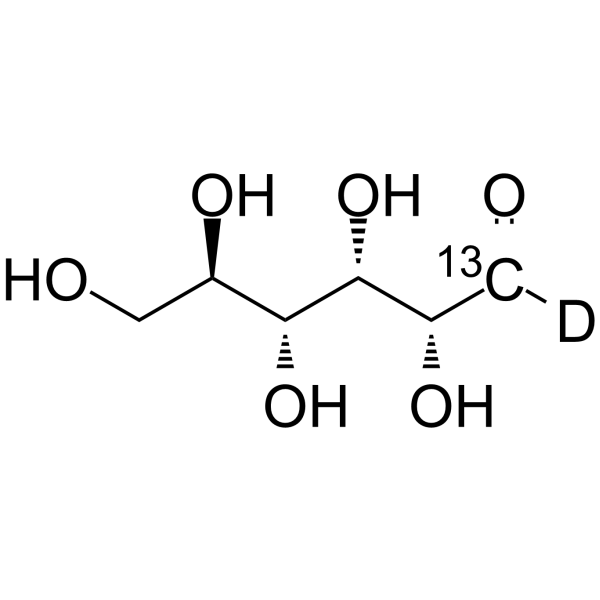
-
- HY-W010042S1
-
|
L-(-)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-1
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Glucose- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose (L-(-)-Glucose) is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose can promote food intake[1][2].
|
-
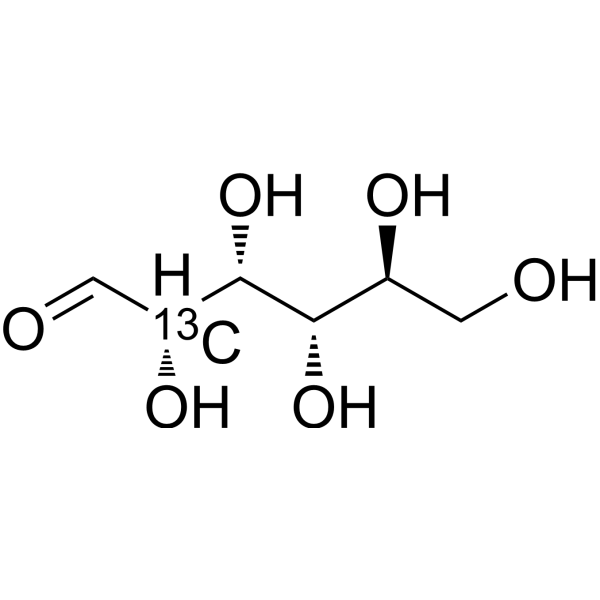
-
- HY-W010042S2
-
|
L-(-)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-2
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Glucose- 13C-2 is the 13C labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose (L-(-)-Glucose) is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose can promote food intake[1][2].
|
-
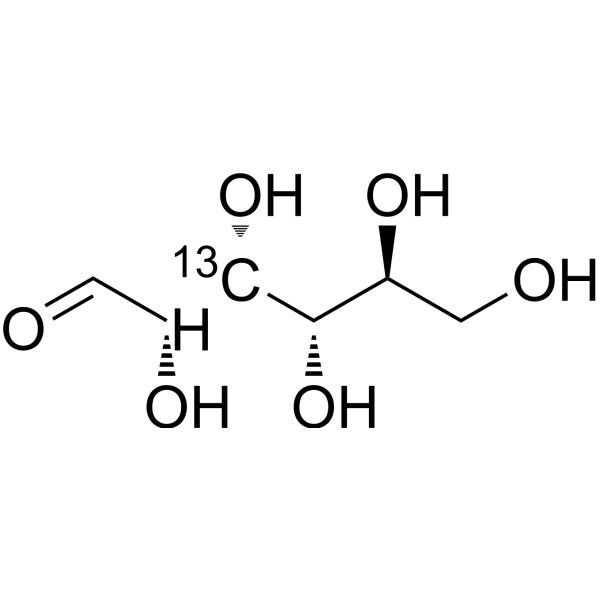
-
- HY-B0389A
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C6; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C6; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C6
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C6 is a stable isotope-labeled counterpart of D-glucose (HY-B0389). D-Glucose- 13C6 can be used as a metabolic tracer to trace glucose-related synthetic catabolism or as synthesis ingredient, minimal media reagent, and internal standard .
|
-
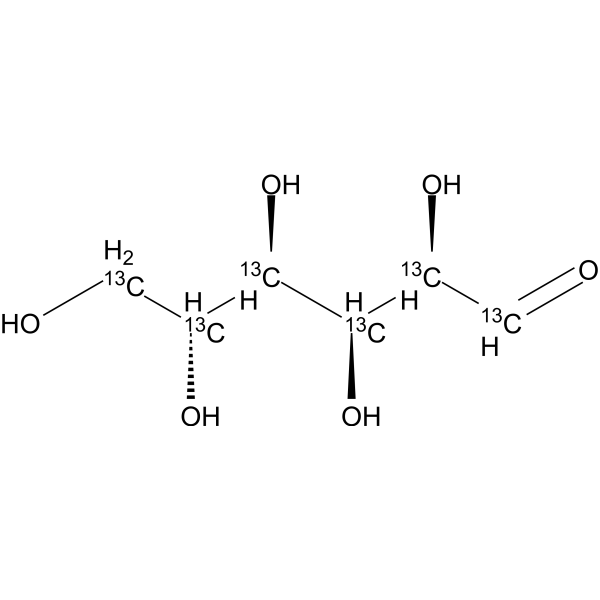
-
- HY-B0389S14
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C2
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C2 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
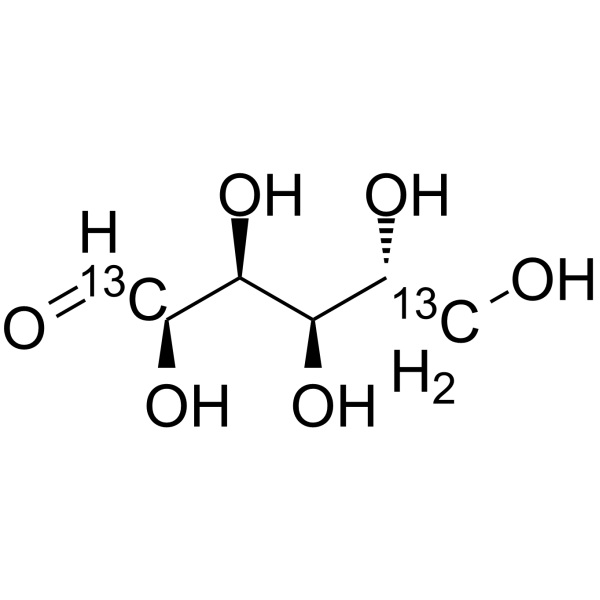
-
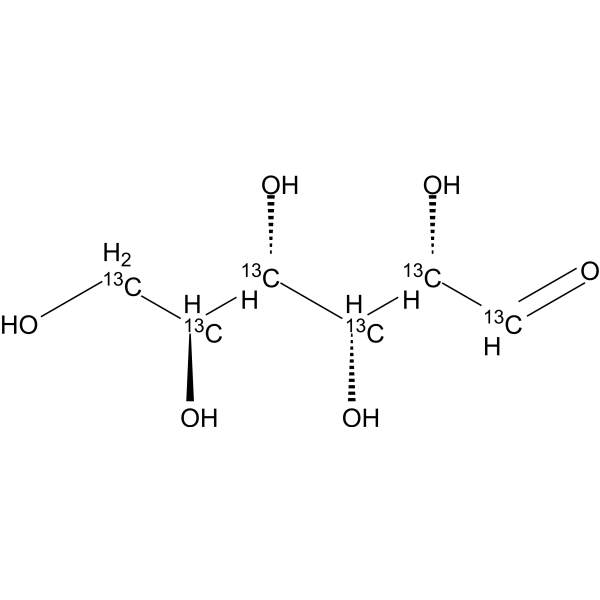
- HY-W010042S3
-
-
-
- HY-B0389S18
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C3-1; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C3-1; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C3-1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C3-1 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
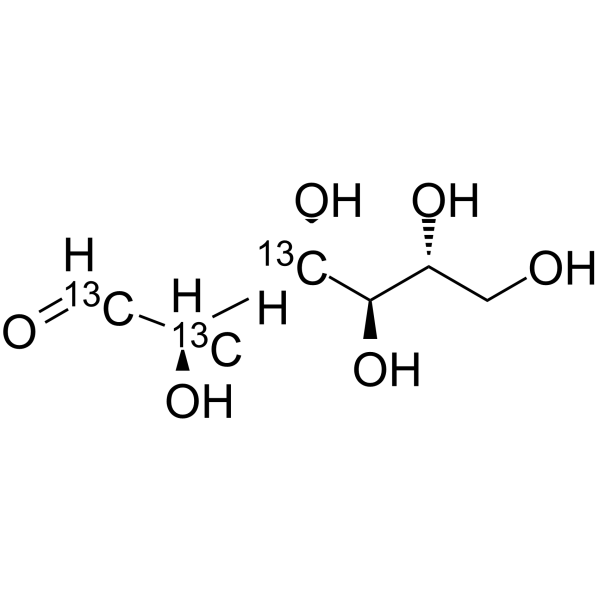
-
- HY-B0389S15
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2-4; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2-4; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C2-4
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C2-4 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
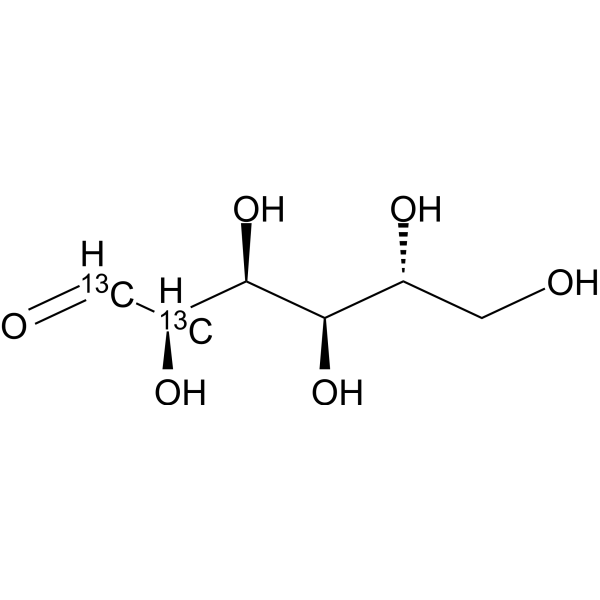
-
- HY-B0389S9
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C3-2; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C3-2; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C3-2
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C3-2 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-
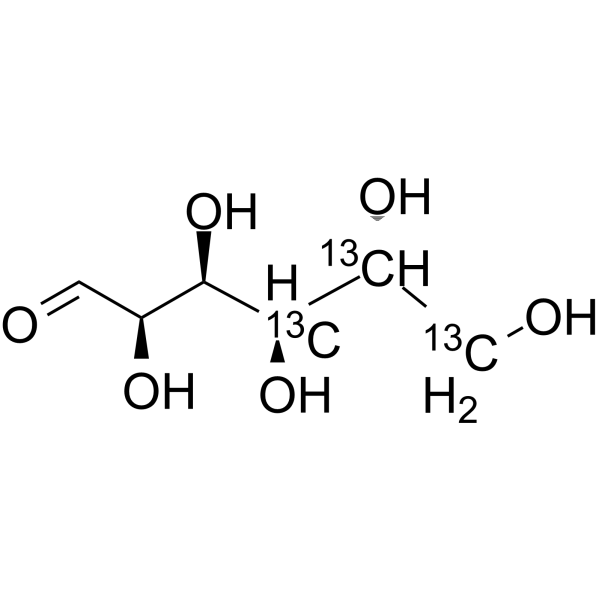
-
- HY-B0389S21
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,d2; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,d2; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C,d2
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
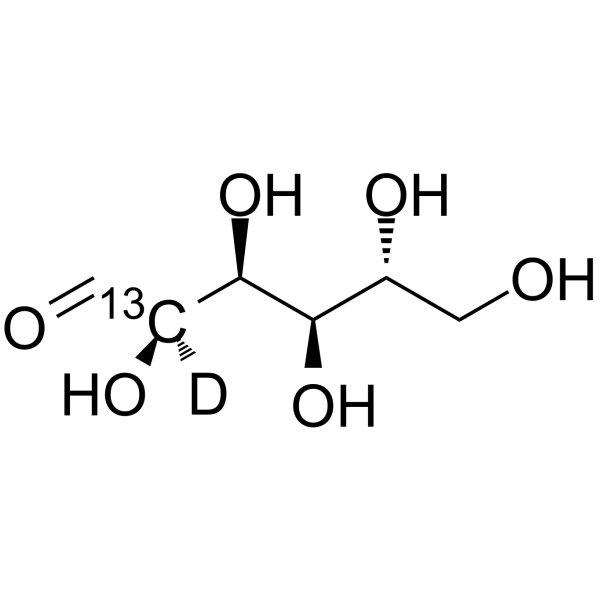
D-Glucose- 13C,d2 is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical sig
|
-
-
- HY-B0389S25
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,d1; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,d1; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C,d1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
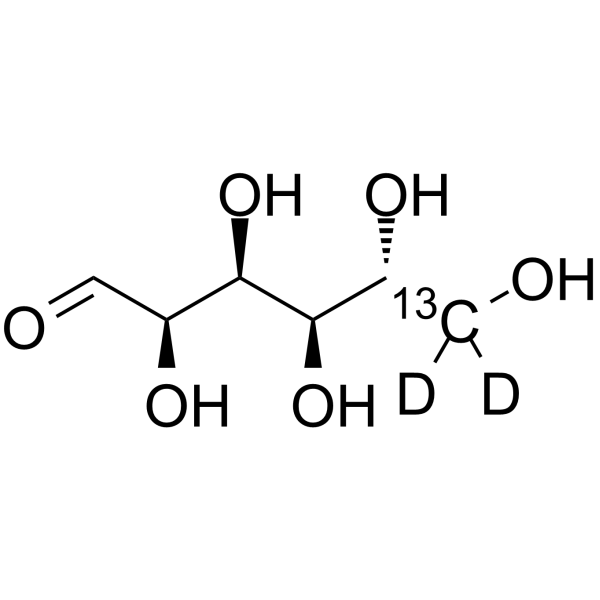
D-Glucose- 13C,d is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical sig
|
-
-
- HY-B0389S
-
-
-
- HY-B0389S22
-
|
Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2,d2; D-(+)-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2,d2; Dextrose-<sup>13sup>C2,d2
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
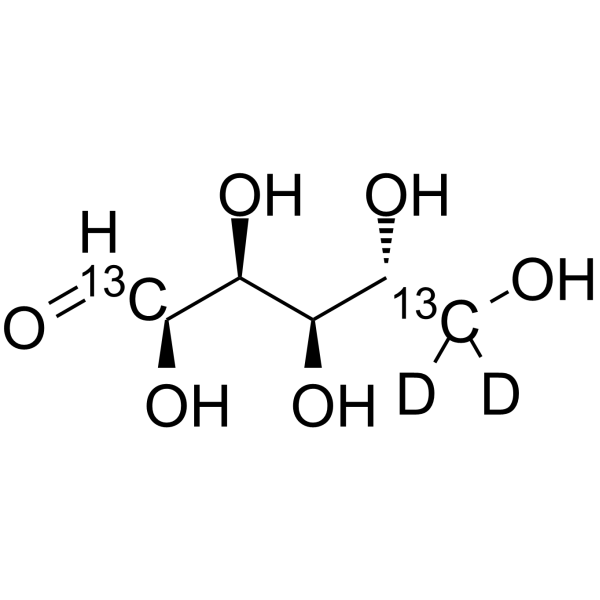
D-Glucose- 13C2,d2 is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical si
|
-
-
- HY-N7032S
-
-
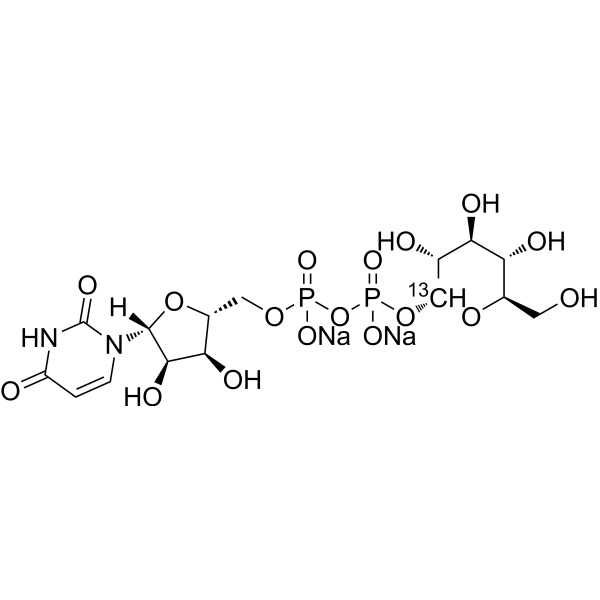
-
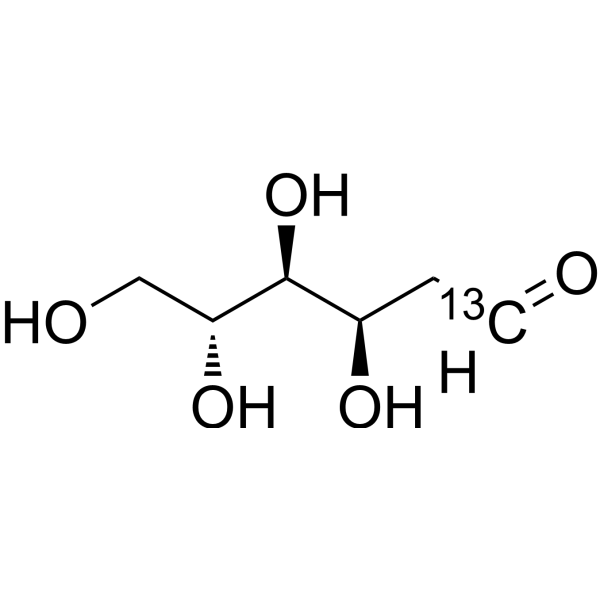
- HY-13966S2
-
|
2-DG-<sup>13sup>C; 2-Deoxy-D-arabino-hexose-<sup>13sup>C; D-Arabino-2-deoxyhexose-<sup>13sup>C
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Apoptosis
Hexokinase
HSV
|
Cancer
|
|
2-Deoxy-D-glucose- 13C is the 13C labeled 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose is a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism, inhibiting glycolysis via its actions on hexokinase[1][2].
|
-
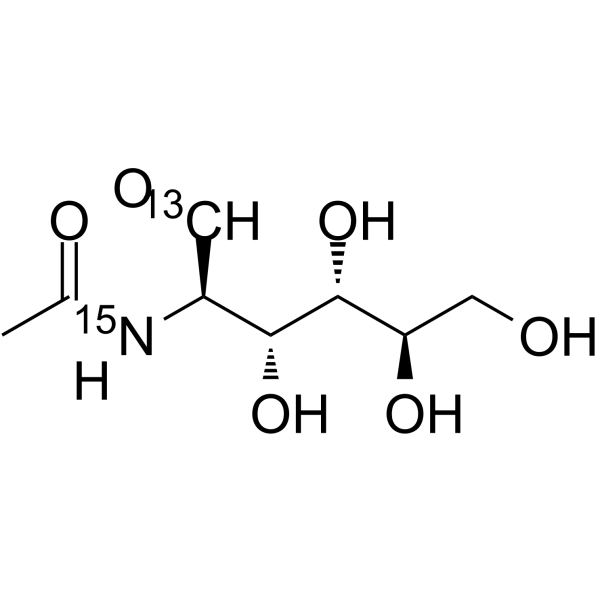
-
- HY-A0132S8
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,<sup>15sup>N
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C, 15N is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
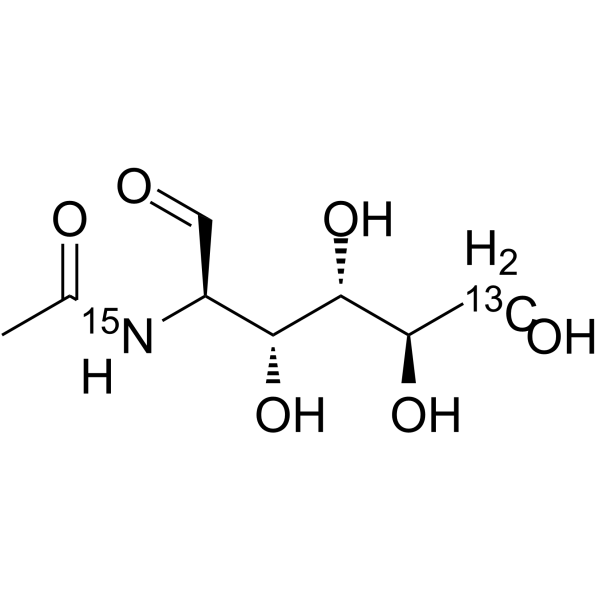
-
- HY-A0132S11
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C,<sup>15sup>N-1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C, 15N-1 is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-A0132S4
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>18sup>O
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 18O is the 18O labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
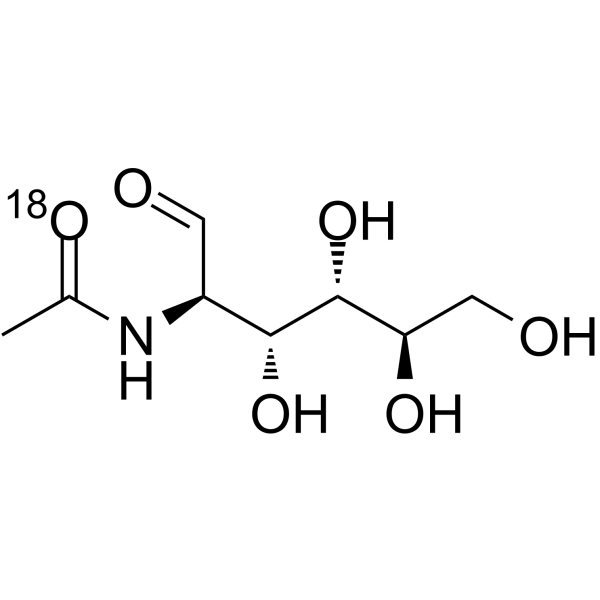
-
- HY-A0132S1
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
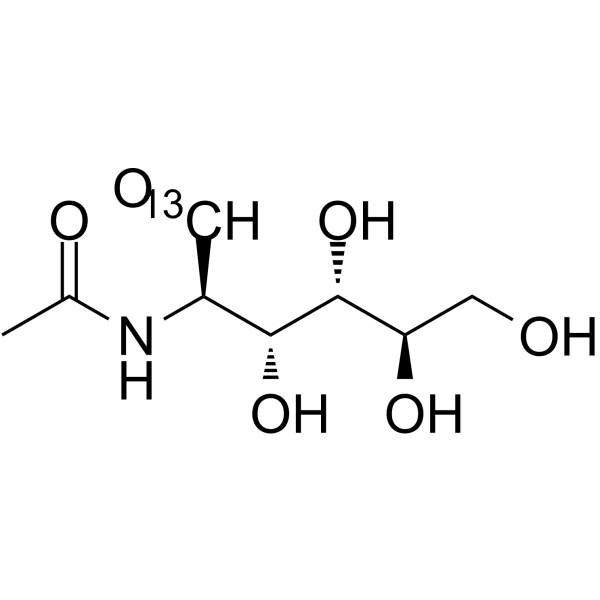
-
- HY-A0132S7
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>15sup>N
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 15N is the 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
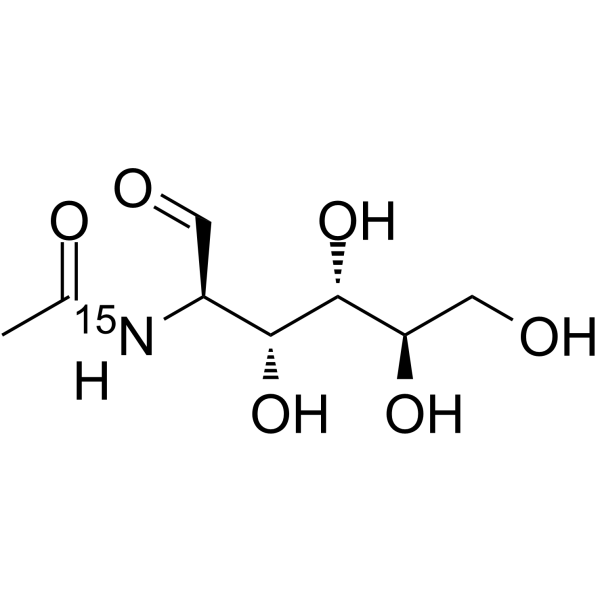
-
- HY-N7032S1
-
|
UDP-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C6 disodium
|
P2Y Receptor
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose- 13C6 (disodium) is the 13C labeled Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose disodium salt[1]. Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose disodium salt (UDP-D-Glucose disodium salt) is the precursor of glucose-containing oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids in animal tissues and in some microorganisms. Uridine-5′-diphosphoglucose is an agonist of the P2Y14 receptor, a neuroimmune system GPCR[2].
|
-
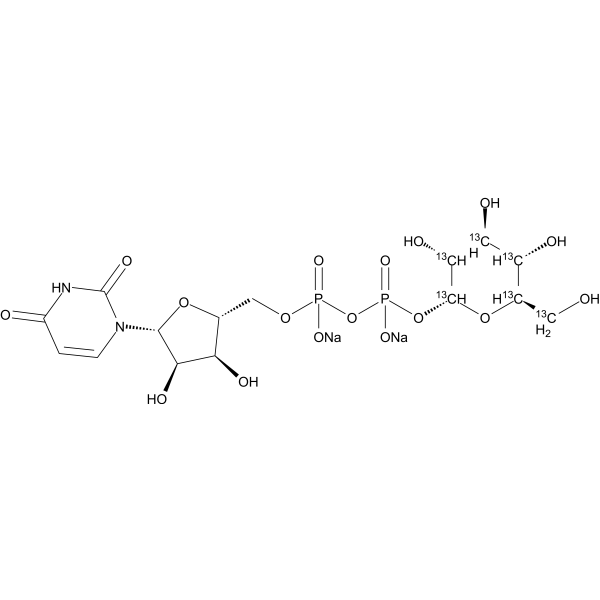
-
- HY-13966S4
-
|
2-DG-<sup>13sup>C-1; 2-Deoxy-D-arabino-hexose-<sup>13sup>C-1; D-Arabino-2-deoxyhexose-<sup>13sup>C-1
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Apoptosis
Hexokinase
HSV
|
Cancer
|
|
2-Deoxy-D-glucose- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose is a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism, inhibiting glycolysis via its actions on hexokinase[1][2].
|
-
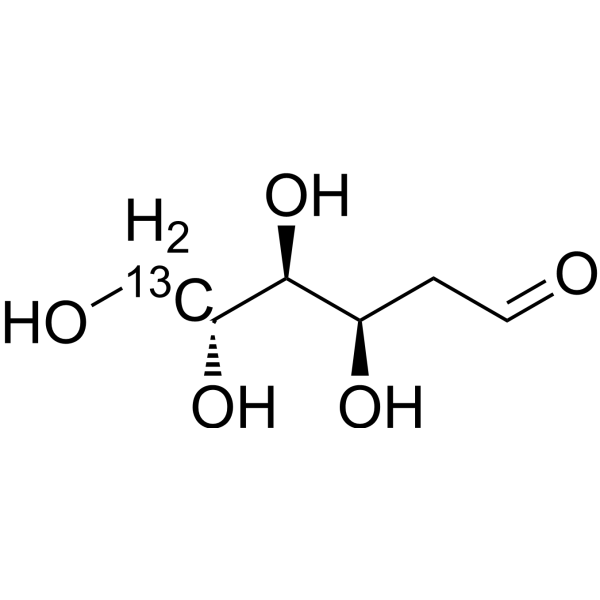
-
- HY-A0132S9
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C3,<sup>15sup>N
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C3, 15N is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
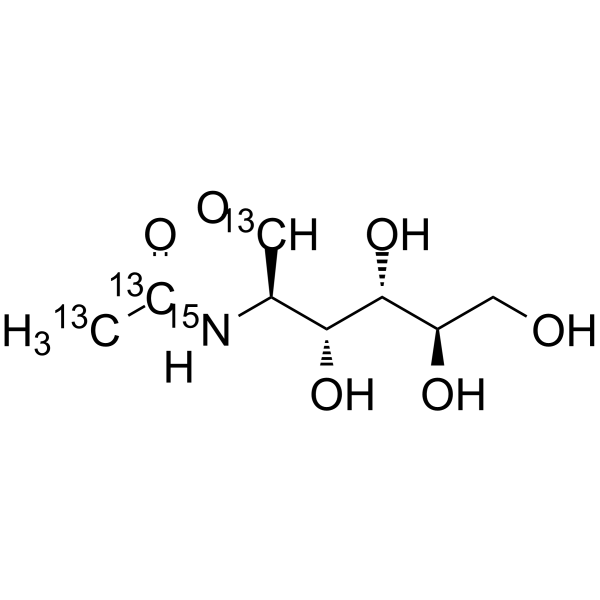
-
- HY-A0132S10
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C2,<sup>15sup>N
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C2, 15N is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
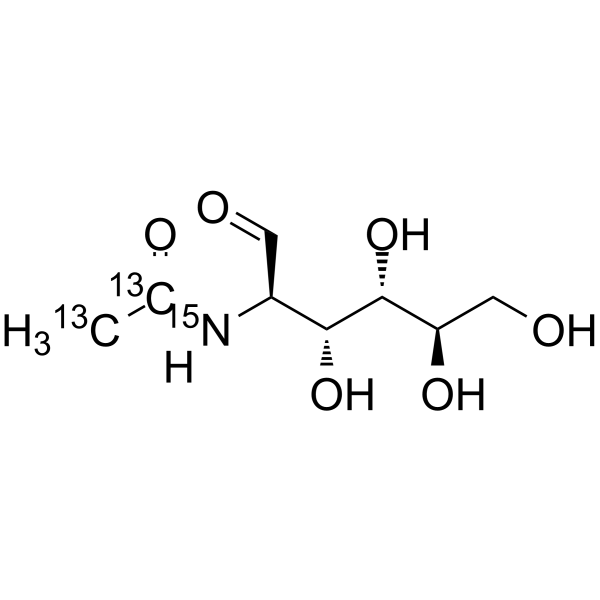
-
- HY-A0132S13
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C8,<sup>15sup>N
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Others
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C8, 15N is 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine (HY-A0132). N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose.
|
-
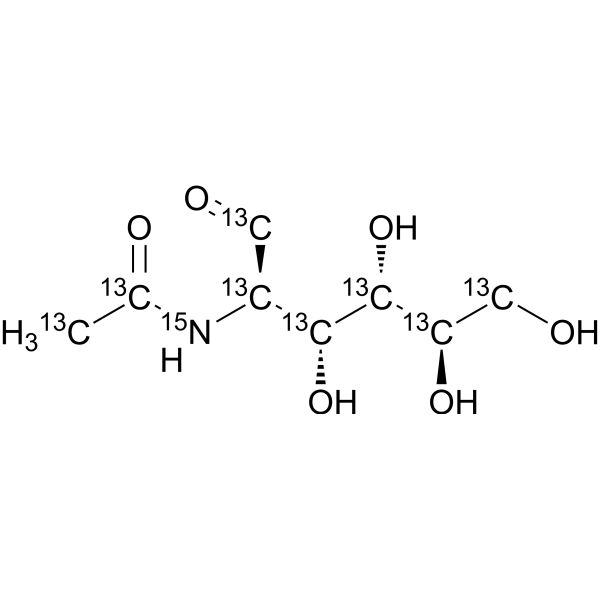
-
- HY-A0132S2
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
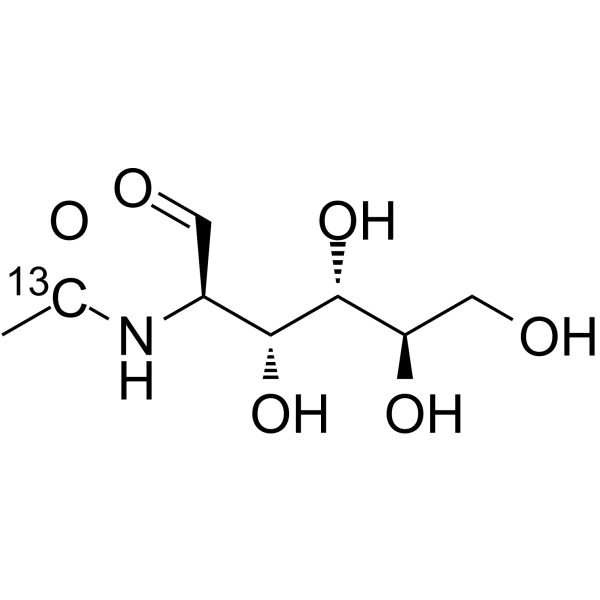
-
- HY-A0132S3
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-2
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C-2 is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
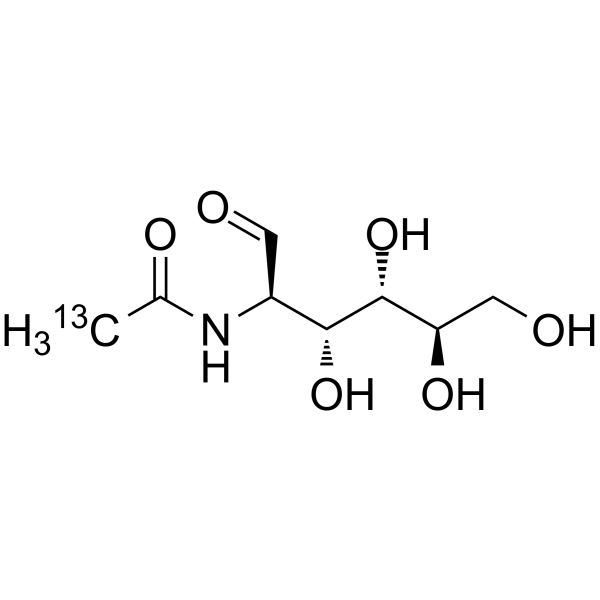
-
- HY-A0132S5
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C-3
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C-3 is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-
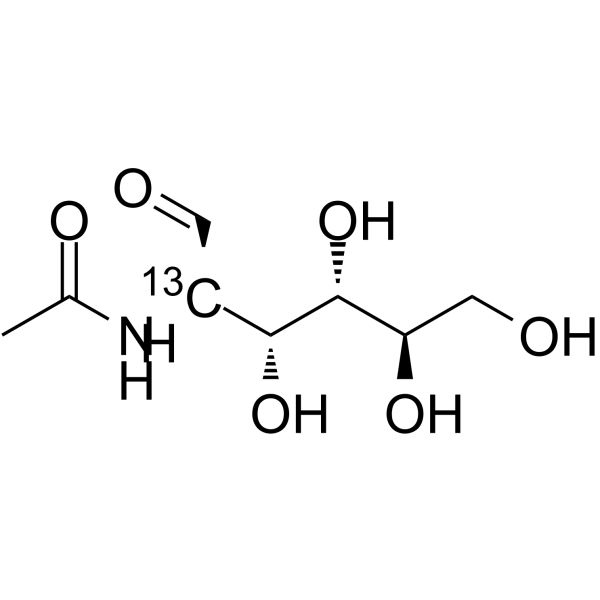
-
- HY-W050145S2
-
|
1,6-Anhydro-β-D-glucopyranose-<sup>13sup>C6; 1,6-Anhydro-β-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C6
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Levoglucosan- 13C6 is the 13C labeled Levoglucosan[1]. Levoglucosan (1,6-Anhydro-β-D-glucopyranose) is an anhydrosugar produced through glucan pyrolysis and is widely found in nature[2].
|
-
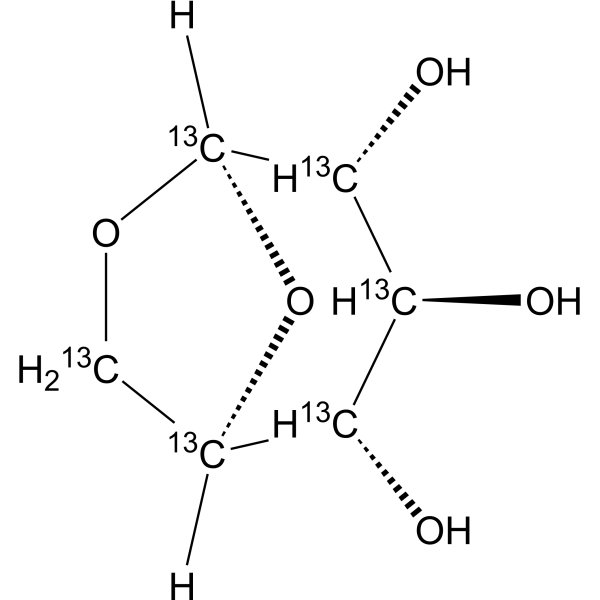
-
- HY-A0132S12
-
|
N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-Glucose-<sup>13sup>C6
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C6 (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose- 13C6) is the 13C labled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine (HY-A0132) . N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose.
|
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B0389S10
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-W010042S
-
|
|
|
L-Glucose- 13C is the 13C labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose (L-(-)-Glucose) is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose can promote food intake[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S29
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S11
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S12
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-2 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S16
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-4 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S17
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-5 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S13
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C-3 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S30
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O-1 is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecule
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S31
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O-2 is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecule
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S32
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 18O-3 is the 18O labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecule
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S19
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C,d is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical sign
|
-

-
- HY-W010042S1
-
|
|
|
L-Glucose- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose (L-(-)-Glucose) is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose can promote food intake[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-W010042S2
-
|
|
|
L-Glucose- 13C-2 is the 13C labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose (L-(-)-Glucose) is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose can promote food intake[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389A
-
3 Publications Verification
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C6 is a stable isotope-labeled counterpart of D-glucose (HY-B0389). D-Glucose- 13C6 can be used as a metabolic tracer to trace glucose-related synthetic catabolism or as synthesis ingredient, minimal media reagent, and internal standard .
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S14
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C2 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-W010042S3
-
|
|
|
L-Glucose- 13C6 (L-(-)-Glucose- 13C6) is C13-labeled L-Glucose. L-Glucose is an enantiomer of D-glucose. L-Glucose enhances food intake .
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S18
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C3-1 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S15
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C2-4 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S9
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C3-2 is the 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical signaling molecules in relation to both cellular metabolic status and biotic and abiotic stress response[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S21
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C,d2 is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical sig
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S25
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C,d is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical sig
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S
-
|
|
|
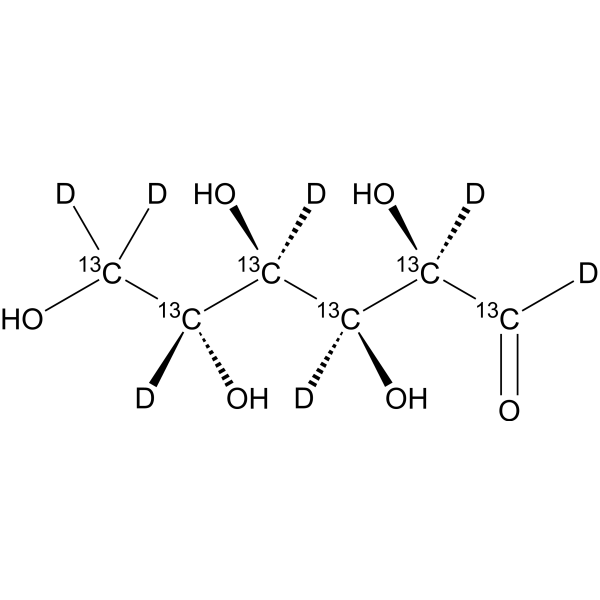
D-Glucose- 13C6,d7 is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0389S22
-
|
|
|
D-Glucose- 13C2,d2 is the deuterium and 13C labeled D-Glucose. D-Glucose (Glucose), a monosaccharide, is an important carbohydrate in biology. D-Glucose is a carbohydrate sweetener and critical components of the general metabolism, and serve as critical si
|
-

-
- HY-N7032S
-
|
|
|
Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose- 13C (disodium) is the 13C labeled Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose disodium salt. Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose disodium salt (UDP-D-Glucose disodium salt) is the precursor of glucose-containing oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycop
|
-

-
- HY-13966S2
-
|
|
|
2-Deoxy-D-glucose- 13C is the 13C labeled 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose is a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism, inhibiting glycolysis via its actions on hexokinase[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S8
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C, 15N is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S11
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C, 15N-1 is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S4
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 18O is the 18O labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S1
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S7
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 15N is the 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-N7032S1
-
|
|
|
Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose- 13C6 (disodium) is the 13C labeled Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose disodium salt[1]. Uridine 5′-diphosphoglucose disodium salt (UDP-D-Glucose disodium salt) is the precursor of glucose-containing oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids in animal tissues and in some microorganisms. Uridine-5′-diphosphoglucose is an agonist of the P2Y14 receptor, a neuroimmune system GPCR[2].
|
-

-
- HY-13966S4
-
|
|
|
2-Deoxy-D-glucose- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose is a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism, inhibiting glycolysis via its actions on hexokinase[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S9
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C3, 15N is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S10
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C2, 15N is the 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S13
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C8, 15N is 13C and 15N labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine (HY-A0132). N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose.
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S2
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C-1 is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S3
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C-2 is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S5
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C-3 is the 13C labeled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of gluc[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-W050145S2
-
|
|
|
Levoglucosan- 13C6 is the 13C labeled Levoglucosan[1]. Levoglucosan (1,6-Anhydro-β-D-glucopyranose) is an anhydrosugar produced through glucan pyrolysis and is widely found in nature[2].
|
-

-
- HY-A0132S12
-
|
|
|
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine- 13C6 (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose- 13C6) is the 13C labled N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine (HY-A0132) . N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-Acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose.
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent:

















































